Remote access to Raspberry Pi IoT devices has become a critical skill for modern tech enthusiasts and professionals alike. Whether you're setting up a home automation system, managing a fleet of IoT devices, or simply tinkering with your Raspberry Pi, having the right tools and knowledge is essential. This guide will walk you through the best options for remote access, helping you download the right software and set up your Raspberry Pi IoT device seamlessly.
In today's interconnected world, IoT devices powered by Raspberry Pi are revolutionizing how we interact with technology. From smart homes to industrial applications, the possibilities are endless. However, effective remote access is key to unlocking their full potential. This article aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the best tools and methods to achieve this.
By the end of this guide, you'll not only know how to download and install the necessary software but also understand the best practices for secure and efficient remote access. Let's dive in!
Read also:John Mcphee Military Career A Detailed Exploration
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Remote Access Raspberry Pi IoT
- Best Tools for Remote Access
- How to Download and Install Software
- Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi for Remote Access
- Securing Your IoT Devices
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Comparison of Popular Remote Access Tools
- Optimizing Performance
- Real-World Applications
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to Remote Access Raspberry Pi IoT
Why Remote Access Matters
Remote access allows you to control and manage your Raspberry Pi IoT devices from anywhere in the world. This capability is particularly useful for monitoring, troubleshooting, and maintaining devices without needing physical access. Whether you're a hobbyist or a professional, understanding remote access is essential for maximizing the functionality of your IoT setup.
Key benefits include:
- Convenience: Manage devices from any location.
- Efficiency: Resolve issues faster without delays.
- Scalability: Easily manage multiple devices.
Best Tools for Remote Access
Popular Options for Raspberry Pi IoT
There are several tools available for remote access to Raspberry Pi IoT devices. Below are some of the best options:
- SSH (Secure Shell): A secure protocol for accessing your Raspberry Pi via command line.
- VNC (Virtual Network Computing): Enables graphical remote access, allowing you to interact with the desktop environment.
- TeamViewer: A user-friendly option that supports both command-line and graphical interfaces.
- ngrok: A tunneling tool that provides secure access over the internet.
How to Download and Install Software
Step-by-Step Guide
Downloading and installing the right software is crucial for setting up remote access. Follow these steps:
- Visit the official website of the chosen tool (e.g., TeamViewer).
- Download the appropriate version for your Raspberry Pi operating system (e.g., Raspbian).
- Transfer the downloaded file to your Raspberry Pi using a USB drive or SCP.
- Install the software by running the installation script in the terminal.
Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi for Remote Access
Configuring SSH
SSH is one of the most widely used methods for remote access. To enable it:
- Open the terminal on your Raspberry Pi.
- Type
sudo raspi-configand navigate to "Interfacing Options." - Select "SSH" and enable it.
- Reboot your Raspberry Pi for the changes to take effect.
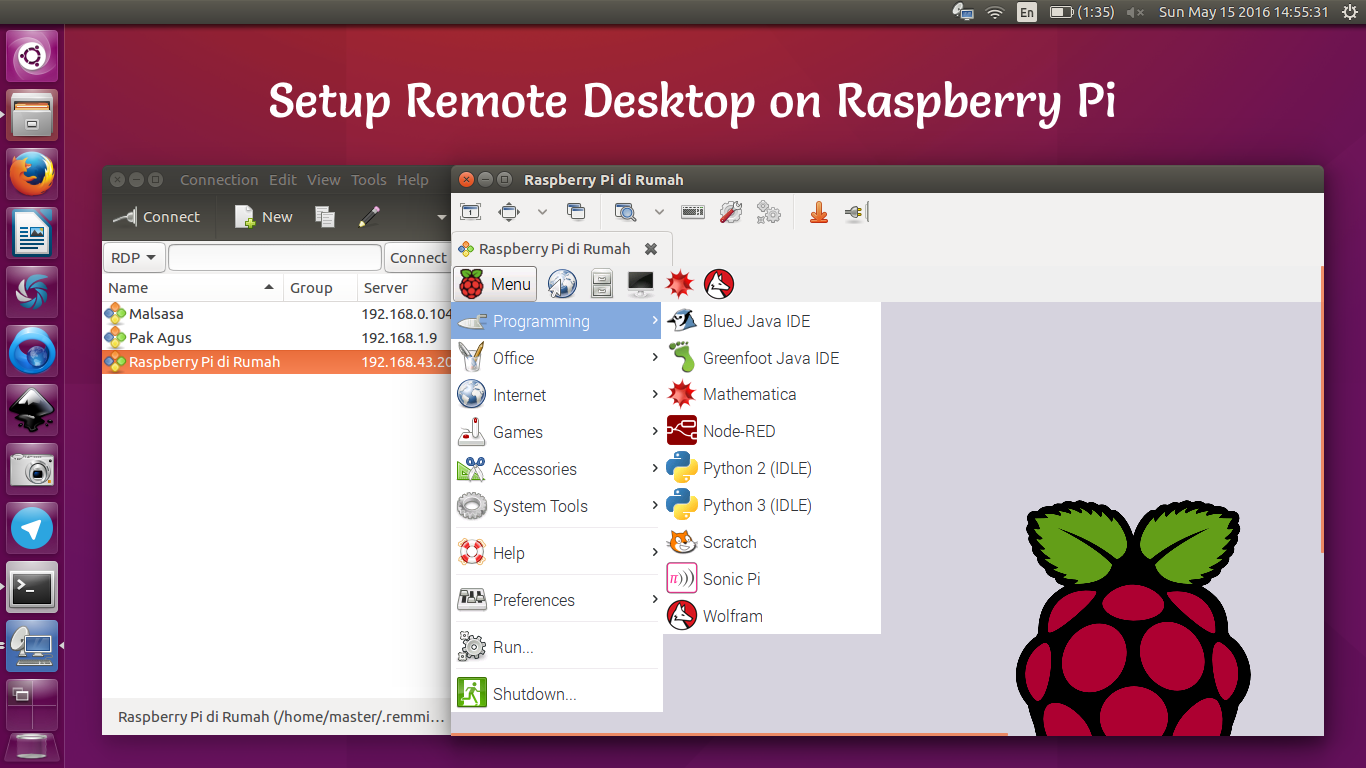
Configuring VNC
VNC provides a graphical interface for remote access. Here's how to set it up:
Read also:Hdhub4uphd Your Ultimate Guide To Highquality Movies And Tv Shows
- Install the VNC Server on your Raspberry Pi by running
sudo apt-get install realvnc-vnc-server realvnc-vnc-viewer. - Enable VNC through the Raspberry Pi configuration menu.
- Download the VNC Viewer app on your remote device.
Securing Your IoT Devices
Best Practices for Security
Security is paramount when it comes to remote access. Follow these best practices:
- Use strong, unique passwords for all devices.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) where possible.
- Regularly update your software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Limit access to trusted IP addresses if feasible.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Resolving Connection Problems
Encountering issues with remote access? Here are some common problems and solutions:
- Connection Refused: Ensure that the SSH or VNC service is running.
- Authentication Failed: Double-check your username and password.
- Network Issues: Verify your network settings and ensure your Raspberry Pi is connected to the internet.
Comparison of Popular Remote Access Tools
Feature Comparison
Choosing the right tool depends on your specific needs. Below is a comparison of popular options:
| Tool | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSH | Command-line access | Secure, lightweight | No graphical interface |
| VNC | Graphical interface | User-friendly | Higher resource usage |
| TeamViewer | Multi-platform support | Easy setup | Potential privacy concerns |
Optimizing Performance
Tips for Better Performance
To ensure smooth remote access, consider these optimization tips:
- Use a fast and stable internet connection.
- Minimize background processes on your Raspberry Pi.
- Optimize your VNC settings for lower latency.
Real-World Applications
Examples of IoT Projects
Raspberry Pi IoT devices have countless applications. Some examples include:
- Smart home automation systems.
- Environmental monitoring solutions.
- Industrial automation and control systems.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, mastering remote access for Raspberry Pi IoT devices opens up a world of possibilities. By selecting the right tools, following best practices, and ensuring security, you can effectively manage your devices from anywhere. We encourage you to:
- Experiment with different tools to find what works best for you.
- Stay updated with the latest developments in IoT technology.
- Share your experiences and insights in the comments section below.
Thank you for reading! If you found this guide helpful, consider exploring our other articles on IoT and Raspberry Pi. Happy tinkering!
References: